There is the problem that is bothering me with the black hole evaporation because of Hawking radiation.
According to Hawking theory the black hole will evaporate in finite time because of quantum effects randomly producing particle-antiparticle pairs on the opposite sites of horizon.
However, the gravity causes the time dilatation, which goes to infinity on the horizon itself, so the arbitrarily small amount of time from horizon's perspective is going to be infinitely long from external observer's perspective?
So, from which perspective is the time the black hole will evaporate calculated? If it is calculated from horizon's perspective, it would mean, the black hole will never evaporate from the external observer's perspective?
Answer
If we refer to the evaporating black hole's Penrose diagram
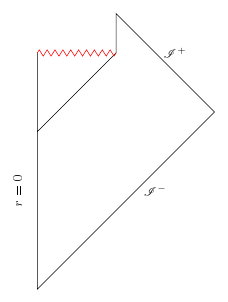
we would see some important differences between the ideal and the evaporating black holes. For the evaporating black hole, there is a moment in spacetime, where the horizon (and the singularity) disappears, mass left at the center of coordinates is zero, and no time dilatation is left. Hense, this event can be seen for every external observer with no problem.
No comments:
Post a Comment